China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载
As a result of weak demand and subdued energy prices, EMDE inflation has fallen below central bank targets, on average, since May (figures 1.21.A and 1.21.B). Nevertheless, the fall in inflation in EMDEs has been less broad based than in advanced economies, reflecting the effects of sharp currency depreciations as well as rising domestic food prices in some countries (Ebrahimy, Igan, and Martinez Peria 2020). Whereas underlying inflationary pressures in most EMDEs are likely to remain subdued amid persistently soft demand, negative output gaps following the collapse in activity may not be as sizable as currently envisioned due to the pandemic’s damage to potential growth.
This could eventually fuel a pickup in inflation. Central bank policy rates have mostly remained stable at very accommodative levels (figure 1.21.C). The prospect of generally contained inflationary pressures, along with recent changes to the monetary policy framework of the U.S. Federal Reserve that is likely to keep U.S. policy rates low for an extended period, may enable a number of EMDE central banks to maintain their accommodative policy stances during the recovery (Arteta et al. 2015; Kose, Nagle et al. 2020). Lower borrowing costs could also help lessen the financing burden on EMDEs with high debt loads and associated financial risks. These benefits may, however, be elusive for those EMDEs facing lingering vulnerabilities, such as large external imbalances or dwindling reserve buffers.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
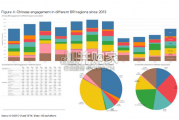
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 52 英文报告下载
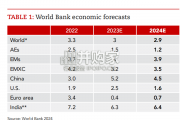
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 96 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 67 英文报告下载
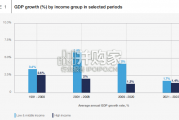
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
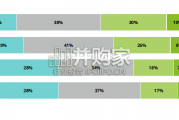
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言