The NSTC will also convene a technical advisory board from industry,...
2024-08-08 27 英文报告下载
The frst pillar of the Bretton Woods institutions, fnancial stability, is anchored by the IMF. The international monetary system that emerged at Bretton Woods flled a critical gap in the global economy. The IMF, the only global, multilateral rules-based institution providing balance of payment support, is crucial for maintaining international fnancial stability and preventing fnancial crisis contagion in a highly globalized system (Rodrik and Subramanian 2009; Obstfeld 2009). According to our research and the broader literature, the IMF has contributed to global fnancial stability in a number of ways, for example, by providing liquidity to countries in need or by conducting economic surveillance (Stiglitz 2011; Bradlow and Gallagher 2021). Over the past two decades, there has been a proliferation of alternative sources of liquidity fnance for certain countries to combat balance of payment crises (Kring and Gallagher 2019; Kring and Grimes 2019; Muhlich et al. 2022; Barrowclough et al. 2022). As Figure 1 shows, currently, the IMF represents less than one-third of the Global Financial Safety Net (GFSN) - the network of institutions aimed at supporting countries during times of fnancial distress including the IMF, regional fnancial arrangements (RFAs) and bilateral credit lines provided by central banks called currency swaps. While the emergence and expansion of RFAs and central bank currency swap lines have contributed to a diversifed GFSN, lower income countries are largely excluded from these resources (Mühlich et al. 2022). The systemic bias against lower-income countries in currency swaps arises from the economic, trade, fnancial and political considerations of the central banks providing these swaps in relation to the recipient countries (Goda et al. 2024). Moreover, the lack of an African RFA contributes to this bias (Dagah et al. 2019). At a minimum, the IMF ensures that economies not considered systemically important have a lender to turn to in times of crisis, though the sufciency of these resources may be limited (Mühlich et al. 2022; Goda et al. 2024).

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
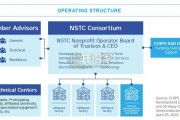
The NSTC will also convene a technical advisory board from industry,...
2024-08-08 27 英文报告下载
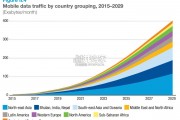
Video traffc is estimated to account for almost three quarters of all...
2024-08-05 22 英文报告下载
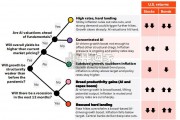
We use scenarios to help identify where economies and markets may be...
2024-07-25 45 英文报告下载

The world’s population is expected to continue growing over the coming fift...
2024-07-23 20 英文报告下载

The near-term growth prospects for major economies diverge. The outlo...
2024-07-22 35 英文报告下载
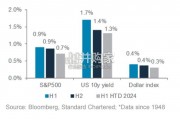
In the US, our equity sector Overweights are focused on the technolog...
2024-07-18 28 英文报告下载
最新留言