China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载
Online learning: – More than 50 million students across 30 provinces attended classes on DingTalk, Alibaba’s enterprise messaging app, on the first day of the semester on Feb 10 – Online classroom service provider EEO’s platform, ClassIn, used to host about 200,000 students daily before the epidemic but now sees an average of two million students a day New formats of instruction: China’s prestigious schools like Tsinghua University offered online courses to anyone on short video app Douyin during the outbreak Online patient consulting: – Ping An Good Doctor, China’s largest healthcare platform, received 10x sign-ups between 22 January to 6 February, compared with the same period in 2018 – Tencent Trusted Doctors offered online consultation to Wuhan residents, quadrupling its consultations during the first five days of the Lunar New Year, compared with the same period last year Knowledge sharing: The Global MediXchange for Combating COVID-19 (GMCC) program was established by the Alibaba Foundation and Jack Ma Foundation to facilitate sharing of best practices and knowledge for fighting the pandemic among medical professionals around the world in real-time in 11 languages.
In August 2019, Huawei announced plans to invest US$1.4bn in a massive new R&D center in Shanghai, estimated to house 30,000 to 40,000 employees Also in August 2019, Huawei officially announced its homegrown smartphone operating system – Harmony OS – to be used if it loses access to the Android operating system under a US trade ban Over 90% of Huawei phones in China now use processors designed by HiSilicon, the semiconductor company fully owned by Huawei (HiSilicon’s Kirin smartphone processor is considered to be on par with those designed by Apple and Qualcomm).

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
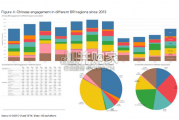
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 52 英文报告下载
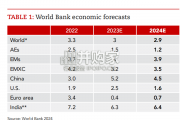
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 96 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 67 英文报告下载
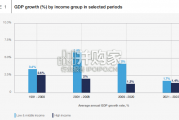
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
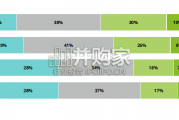
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言