China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载
The size of the global ultra high net worth (UHNW) population — individuals with a net worth above $30m — rose by 1.7% in 2020 to 295,450 individuals. This was a much slower pace of expansion than near double-digit growth a year earlier, and masked large regional and sectoral diferences, but was a resilient performance nonetheless amid the upheaval of the Covid-19 pandemic — national lockdowns, international travel bans, trade disruption and the deepest contraction in world economic output for a generation. Huge monetary stimulus from global central banks and expansive government intervention drove a strong rally in fnancial markets after an initial pandemic-driven slump. With late-year vaccine progress also bolstering investor sentiment and ‘risk-on’ assets, almost all major stock market indices posted healthy annual returns. Overall, the combined net worth of the UHNW population in 2020 increased by 2% to $35.5trn.
Ultra wealth gains may have accrued at a global level, but there were signifcant regional variations in UHNW performance in 2020, refecting contrasting outcomes in terms of public health, economic disruption, policy intervention, asset values and vaccine progress around the world. For a second consecutive year, the best-performing regions were the two largest wealth hubs of North America and Asia, which recorded solid growth of their UHNW populations and collective net worth (following dynamic wealth creation in 2019). Elsewhere it was a very diferent story, with the other fve regions all posting declines. Ultra wealth in Africa held up fairly well, whereas the Pacifc, Europe and the Middle East all registered sizeable falls that largely erased the previous year’s gains.
The worst performing region by far was Latin America and the Caribbean, whose UHNW population and collective net worth slumped by almost a quarter. The food of fnancial-market liquidity and the accelerated adoption of new technologies in response to the pandemic were key drivers of this diverse regional picture, further accentuating structural imbalances between diferent wealth markets and across the global economy. There were also other infuencing factors, including the US presidential election, a pro-democracy clampdown in Hong Kong, volatile commodity and currency markets, rising protectionism and nationalism, the ongoing fallout from US-China tensions, heightened strains across the Gulf region, and still elevated Brexit uncertainty.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 51 英文报告下载
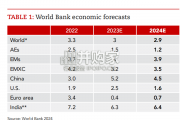
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 96 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 67 英文报告下载
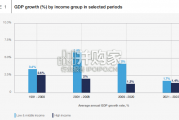
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
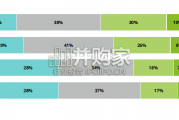
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言