China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载
Hydrogen will play an important role in the global energy transition. It is estimated that hydrogen will account for 10–12 percent of China’s energy consumption by 2050, and as much as 22 percent globally.1 For the country to reach this point sustainably and in line with its emission targets, cheap and scalable green hydrogen technology such as electrolyzers is needed. As costs for carbon-intense fuels increase and electrolysis technology becomes more advanced and efcient,2 green hydrogen is expected to reach price parity with currently cheaper gray hydrogen within a few years. Foreseeable demand, along with the fact that today several technologies compete, means the industry will become not only a lucrative market but also a feld of intense competition, in China and internationally.
China is the world’s largest hydrogen producer with an annual output of 33 million tons, over a third of global demand.3 Hydrogen is used in, among other things, chemical, refning, and metal industries – either as an energy carrier (for example, providing heat or electricity in metallurgy) or as a feedstock (for example, for producing ammonia). While hydrogen is a “clean” energy carrier – reacting with oxygen, it produces only heat and water – producing it can have a signifcant CO2 footprint. China primarily produces brown and gray hydrogen by using coal or gas (respectively 60 percent and 20 percent of production)4 with high CO2 emissions. To meet its targets to achieve peak carbon emissions by 2030 and then reach carbon neutrality by 2060, green hydrogen – currently accounting for about 1 percent of production – will need to replace gray hydrogen as fast as possible (see Exhibit 1).

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
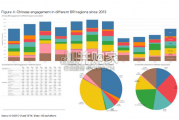
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 51 英文报告下载
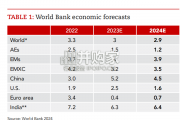
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 96 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 66 英文报告下载
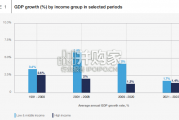
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
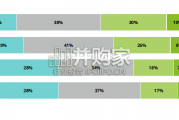
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言