China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 30 英文报告下载
China’s explosive economic growth over the past two decades has been accompanied by extensive foreign investment and financing. According to the China Global Investment Tracker (American Enterprise Institute and Heritage Foundation, 2021), the total of China’s foreign investment and construction from 2005 to 2021 is $2.2 trillion. Until about 2017, Chinese foreign investment and financing had been growing steadily and, in 2022, began increasing again. This foreign investment and financing is driven by a combination of demand for resources (China has the world’s largest population and has been the biggest energy consumer since 2009; U.S. Energy Information Administration, undated), desire to employ Chinese underutilized industrial capacity and workers, and deliberate policy decisions to expand China’s global trade and influence. The two most important such policies are the 1999 Go Out Policy, or the Going Global Strategy, and the 2013 One Belt, One Road, or Belt and Road Initiative (BRI; Chatzky and McBride, 2020; Page, 2018).
China’s foreign investments and financing have raised concerns among Western nations for multiple reasons (Lew and Roughead, 2021; Sutter, Schwarzenberg, and Sutherland, 2021). One is China being relatively less discriminating about the internal politics, global relations, environmental regulations and controls, and human rights, worker safety, and health records of the countries it invests in. Another is claims of unfair contracting practices: Many Chinese firms that bid on foreign investment and financing opportunities are state-owned enterprises that have the backing of the central government and can raise capital more cheaply and offer contract terms that are more competitive than non–government-backed firms from other countries. Still other concerns center on the belief that many Chinese investments and financing are driven less by direct economic returns than by attaining access and influence to wield strategic “soft power” or, in at least one case, establish military footholds. And, recently, evidence of China using disinformation campaigns to influence global critical resource markets has emerged (Mandiant, 2022).

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
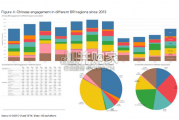
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 30 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 50 英文报告下载
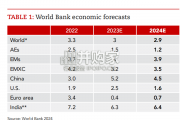
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 95 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 66 英文报告下载
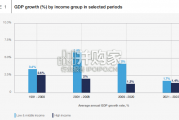
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
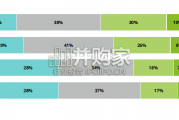
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言