China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 30 英文报告下载
The size of a national stockpile depends on the concept of operations for its development and use (see section 5.3). The quantities of pharmaceutical agents and medical supplies are determined by (a) the anticipated number of casualties, (b) the distribution of injuries requiring urgent or long-term therapy, (c) the medication dosing schedule and (d) the anticipated duration of treatment. It may be difficult to make a realistic estimate of the number of victims requiring medical treatment, as the number of people involved in an incident does not necessarily reflect the number of patients requiring treatment. Furthermore, the density and activity of the population during a radiation incident affect the acuity of medical injuries and the magnitude of the medical response. For example, the release of radioactive material from a low-yield (1 kT) nuclear detonation over a dense urban population may expose hundreds of thousands of individuals to a potentially high dose and/or dose rate of radiation. It may result in tens of thousands of victims requiring emergency treatment and hundreds of thousands requiring psychological and emotional support (Table 1).
The estimates for a higher-yield (10 kT) device are increased by a factor or two or three. The type (or quality) of radiation released (high vs low linear energy transfer) also partly determines the anticipated need. Thus, it has been suggested that approximately 1% of people exposed to radioactive material released from an RDD or “dirty bomb” will require emergent or urgent medical treatment (23). In this case, the number of people requiring emergency treatment may be in the tens and the number of those requiring psychological or emotional support in the thousands or tens of thousands. In the case of exposure to radioactive material released during an NPP accident, millions of people may be exposed to low doses of radiation, as seen after the Chernobyl NPP accident in 1986 (24). In such a scenario, emergency protective actions such as sheltering and limiting consumption of contaminated food and water are more efficient in protecting health and reducing radiation risk. Therefore, the number of MCM and supplies required for a public health and medical response may vary from tens to hundreds of thousands (or possibly millions) of doses and treatments.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
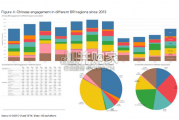
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 30 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 50 英文报告下载
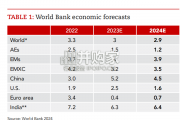
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 95 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 66 英文报告下载
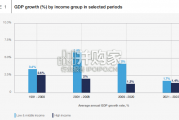
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
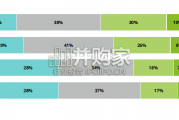
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言