China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载
As of the first week of March, major semiconductor production adjustments have not occurred due to COVID-19 or weak demand for Chinese smartphones. However, some Taiwanese foundries have started to see changes in their capacity utilization for 150mm wafers associated with industrial, consumer electronics, and automotive applications, with a 10ppt reduction in capacity utilization since February. We think this could impact 300mm wafer capacity utilization as smartphone makers revise down their production plans for 2020. Smartphone makers have lowered their production plans for 5G smartphones (from 470−480mn units at the time of our December survey to 380mn units on a bottom-up basis). Consequently, HiSilicon and Samsung LSI—the only 5G chipset vendors whose production plans we have been able to confirm—have dropped their production by 11% (from 520mn to 465mn units).
At this level, there is still disparity between 5G chipset and smartphone production, but this is not particularly worrying given that there is usually a gap of around 15−20% due to the existence of inventory and production lead times. Heading into 2H, however, we expect cutting-edge processes (5nm, 7nm) to remain at full capacity ahead of new product cycles in 5G chipsets, APs (A14) for 2020 iPhone models, AMD processors for the PlayStation 5, and NVidia GPU, where demand is growing for voice recognition applications. Capacity utilization at Samsung Electronics’ CIS lines had fallen by 20–30ppt in 4Q 2019 due to production bottlenecks for CIS stacked with logic, but CIS production has now returned to full capacity thanks to the outsourcing of logic production. We see no major changes overall, but the growing risk of 300mm capacity utilization adjustments is a concern.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
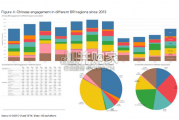
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 52 英文报告下载
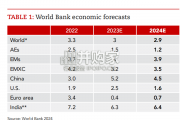
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 96 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 67 英文报告下载
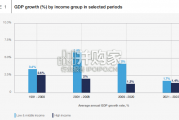
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
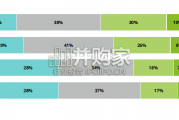
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言