China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载
By conservative estimates, approximately 42 million households do not have internet connections at minimum broadband speeds.33 When millions of Americans cannot reliably access digital opportunities, it has a far-reaching impact. As a foundational issue, struggles with high-speed connectivity impose barriers to information and curb the ability to communicate in public squares, many of which have exclusively transitioned online. Evidenced throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, disparities in access to information can have a devastating impact on households that struggle with reliable internet access while facing other socioeconomic disadvantages. Figure 2 details the demographic makeup of the ten richest and poorest states and territories.
Figure 3 documents which residents face digital inequities, not having a broadband subscription and/or computing device at home. Data shows that the populations who consistently lack access or the tools required to adopt are concentrated in the American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, and Hispanic/Latino columns.Nationwide, Indigenous populations (including Alaskan Native, Native American, and Pacifc Islander), Black/African American, and Hispanic/ Latino American households consistently have the lowest rates of broadband access and adoption. Since limited digital literacy and knowledge about data and technology may prevent some of the most disenfranchised households from being able to advocate for themselves, it is imperative that public policy interventions center on both the impact of disconnectedness and possibilities that could be unlocked with reliable high-speed connectivity.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
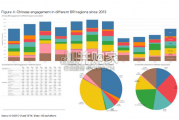
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 51 英文报告下载
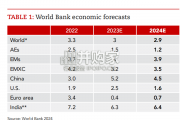
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 96 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 67 英文报告下载
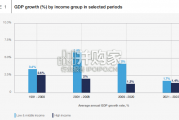
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
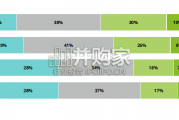
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言