China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载
Trade-policy interventions risk further destabilizing food markets. Ukraine and Russia together represent roughly a quarter of global wheat exports. For corn and fertilizers, their combined pre-war share was almost 15 percent. Disruptions to supplies of these key commodities are causing prices to surge. The price of wheat, for example, has jumped by more than 40 percent since the beginning of the war in late February (with futures prices rising by more than 60 percent). Trade-policy interventions risk making a bad situation worse (Figure 0.2). Export restrictions further reduce global supply, while import liberalization measures and subsidies increase demand. Since the beginning of the war, 53 new trade policies (67 including subsidies) have been imposed or announced. Export restrictions such as outright bans or licensing requirements account for 31 new measures. Export restrictions alone have added seven percentage points to the price of wheat and risk igniting a tit-for-tat escalation that could trigger a food crisis.
Higher food costs take the biggest toll on net importers—largely low and low-middle income countries in Sub-Saharan Africa (Botswana, Zimbabwe) and the Middle East (Algeria, Tunisia)—deepening world poverty.The war and resulting sanctions have disrupted Russian and Ukrainian trade connectivity affecting the logistics of the broader region. Russia’s connections to European ports have been cut, and commodity exports to other destinations have been constrained. Ukraine’s Black Sea ports have been blockaded or occupied, leaving the country few routes for its commodity exports. The war brought reciprocal closures of air space between Russia and 36 countries, resulting in longer routes and higher prices for air freight between Europe and East Asia. Rail transit through Russia may be slowed by additional procedures to check for sanctions compliance, and further rounds of sanctions could risk bringing it to a halt entirely. The role of rail routes in the movement of mechanical, electronics, automotive, and other goods between Europe and Asia (mainly China) is relatively small but has been growing in response to maritime shipping disruptions during the pandemic. Disruptions to global and regional supply chains have caused input shortages and price hikes.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
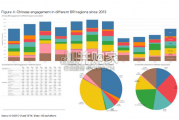
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 51 英文报告下载
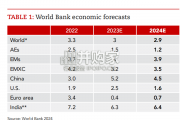
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 96 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 67 英文报告下载
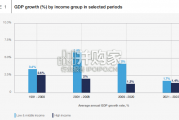
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
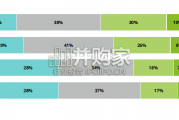
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言