China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 29 英文报告下载
While the low-hanging fruit in trade liberalization has been picked, headwinds have also risen. Rising geopolitical tensions have led to a greater focus on political and national security goals in international trade. Trade restrictions – including tariff and non-tariff barriers – have increased sharply since 2018, with a discernible rise in measures targeting services (see Chart 2). A stark example is the bilateral trade relationship between the U.S. and China. The average U.S. tariff rate vis-a-vis China increased from around 3% to 19% since 2018, with a corresponding rise from 8% to 21% on the part of China. Other recent policies – such as the recent EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism – seek to reshore production which was previously lost due to manufacturing offshoring to avoid domestic carbon taxes (also known as ‘carbon leakage’). There has also been a surge in government subsidies.
For example, the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, worth an estimated USD 369 billion, aims to incentivize firms to manufacture green energy components domestically or in countries which have a free-trade agreement with the U.S. The U.S. Creating Helpful Incentives to Produce Semiconductors and Science (CHIPS) Act, worth USD 280 billion, aims to boost domestic semiconductor manufacturing capacity through a wide range of subsidies and tax incentives. This sparked a response from the European Union in the form of the European Chips Act (worth USD 47 billion), while similar packages were introduced by China, South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan to support their respective domestic semiconductor industries.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
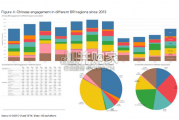
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 29 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 48 英文报告下载
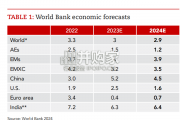
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 95 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 66 英文报告下载
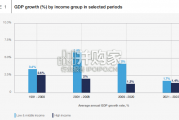
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 81 英文报告下载
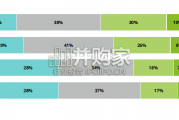
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 65 英文报告下载
最新留言