China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 32 英文报告下载
The three scenarios above have all been positive for the currency in question – even if only marginally. The final scenario we discuss, where loose fiscal policy is accompanied by loose monetary policy, should have a negative currency impact, in theory. This would often be the start of a slippery slope for a currency, for a host of well-worn reasons: potentially higher inflation eroding the value of the currency; likely bond sales by foreign investors causing FX weakness; increased economic imbalances – both in terms of domestic asset bubbles, and externally from a trade perspective; and concerns around monetary policy independence. This negative relationship has held for some currencies in the recent past.
The combined fiscal and monetary expansion in Hungary in 2017-2018 helped to fuel a near 10% move higher in EUR-HUF. The TRY’s struggles in 2018 might have been catalysed by geopolitical developments, but also came against a backdrop of loose policy on both fronts, at a time of high inflation. Italy has also faced challenges when talking of fiscal loosening although this might reflect market concerns about the potential currency mismatch of issuing debt in EUR. In any case, the FX impact of possible fiscal indiscretion in Italy has been fleeting at best. Indeed we are seeing signs that the traditional relationship appears to be breaking down, meaning currencies have been able to withstand this cocktail of loose policies. The most obvious example is South Africa, in our view. South Africa’s fiscal position has been loosening markedly for the last three years and expectations are that this deterioration is only going to continue (Chart 7). This may not be a fiscal loosening in the same sense as seen in the US or Poland. Most of the widening of South Africa’s deficit is a function of poor growth limiting revenue gains and an increasing requirement to provide support to state-owned enterprises (see New Eskom bailout deepens fiscal risks, 25 July 2019). On top of this fiscal loosening, monetary policy has also recently turned more dovish with the SARB delivering a 25bp cut in July and signals of further easing to come.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
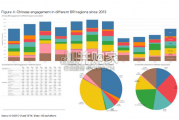
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 32 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 53 英文报告下载
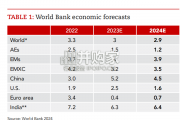
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 99 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 68 英文报告下载
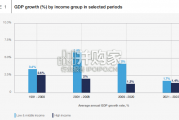
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
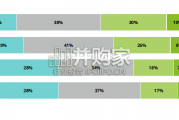
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言